Table of contents
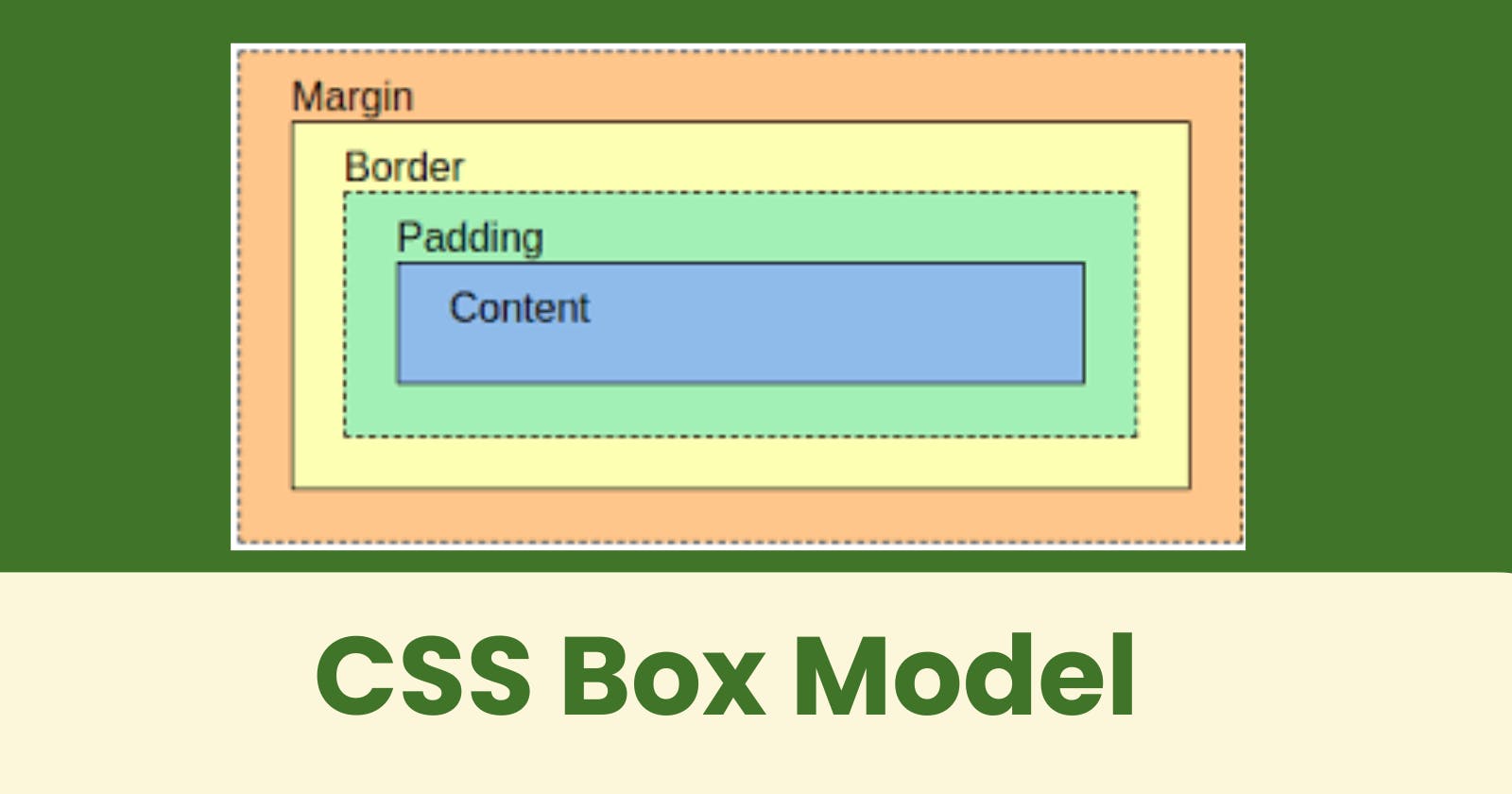
The CSS Box Model is a fundamental concept in web development that defines how HTML elements are rendered on a web page. It is comprised of four main parts:
Explanation of the different parts:
- Content - The content of the box, where text and images appear
- Padding - Clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent
- Border - A border that goes around the padding and content
- Margin - Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent

The box model allows us to add a border around elements, and to define space between elements.
Content Area
The content area, bounded by the content edge, contains the "real" content of the element, such as text, an image, or a video player. Its dimensions are the content width (or content-box width) and the content height (or content-box height). It often has a background color or background image.
If the box-sizing property is set to content-box (default) and if the element is a block element, the content area's size can be explicitly defined with the width, min-width, max-width, height, min-height, and max-height properties.
Padding Area
The padding area, bounded by the padding edge, extends the content area to include the element's padding. Its dimensions are the padding-box width and the padding-box height.
The thickness of the padding is determined by the padding-top, padding-right, padding-bottom, padding-left, and shorthand padding properties.
Border Area
The border area, bounded by the border edge, extends the padding area to include the element's borders. Its dimensions are the border-box width and the border-box height.
The thickness of the borders are determined by the border-width and shorthand border properties. If the box-sizing property is set to border-box, the border area's size can be explicitly defined with the width, min-width, max-width, height, min-height, and max-height properties. When there is a background (background-color or background-image) set on a box, it extends to the outer edge of the border (i.e. extends underneath the border in z-ordering). This default behavior can be altered with the background-clip CSS property.
Margin Area
The margin area, bounded by the margin edge, extends the border area to include an empty area used to separate the element from its neighbors. Its dimensions are the margin-box width and the margin-box height. The size of the margin area is determined by the margin-top, margin-right, margin-bottom, margin-left, and shorthand margin properties. When margin collapsing occurs, the margin area is not clearly defined since margins are shared between boxes.
Finally, note that for non-replaced inline elements, the amount of space taken up (the contribution to the height of the line) is determined by the line-height property, even though the borders and padding are still displayed around the content.
Here are some examples of how the CSS Box Model works with code snippets:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Box Model Example</title>
<style>
div {
background-color: #f2f2f2;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
padding: 20px;
border: 2px solid #000;
margin: 20px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>This is an example of the CSS Box Model.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Conclusion
The CSS Box Model is a crucial concept to understand in web development. By understanding the four parts of the box model (content, padding, border, and margin) and how they interact with each other, developers can create web layouts that are visually appealing and functional. With the help of the code snippets above, you should now have a better understanding of how the CSS Box Model works and how you can use it in your own web development projects.